Secure Software Design and Development
A Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process used by organizations to build an application from its inception to its decommission. It has several phases, from requirement gathering, planning, architecture, coding, testing, release, and maintenance. In the past, security was only considered in the testing phase, which then resulting in after-the-fact techniques to fix the security issues. The Secure SDLC process was introduced to discover and reduce vulnerabilities early on and to ensure security assurance activities such as design review, architecture analysis, code review, and penetration testing are integrated into the development process. There are several SSDLC models available, and here are a few of them (Mougoue, 2017):
- MS Security Development Lifecycle (MS SDL). Microsoft proposed it in association with the phases of a classic SDLC (Microsoft, n.d.).
- NIST 800-64: Provides security considerations within the SDLC (Mougoue, 2017).
- OWASP SAMM (Software Assurance Maturity Model) is the OWASP framework to help organizations assess, formulate, and implement, through the self-assessment model, a strategy for software security that can be integrated into existing SDLC (The SAMM Project team, 2020).
Reflection
In this course, I learned about the general principles of secure software system design, implementation, and analysis, as well as evaluate some of the vulnerabilities present in common software systems.
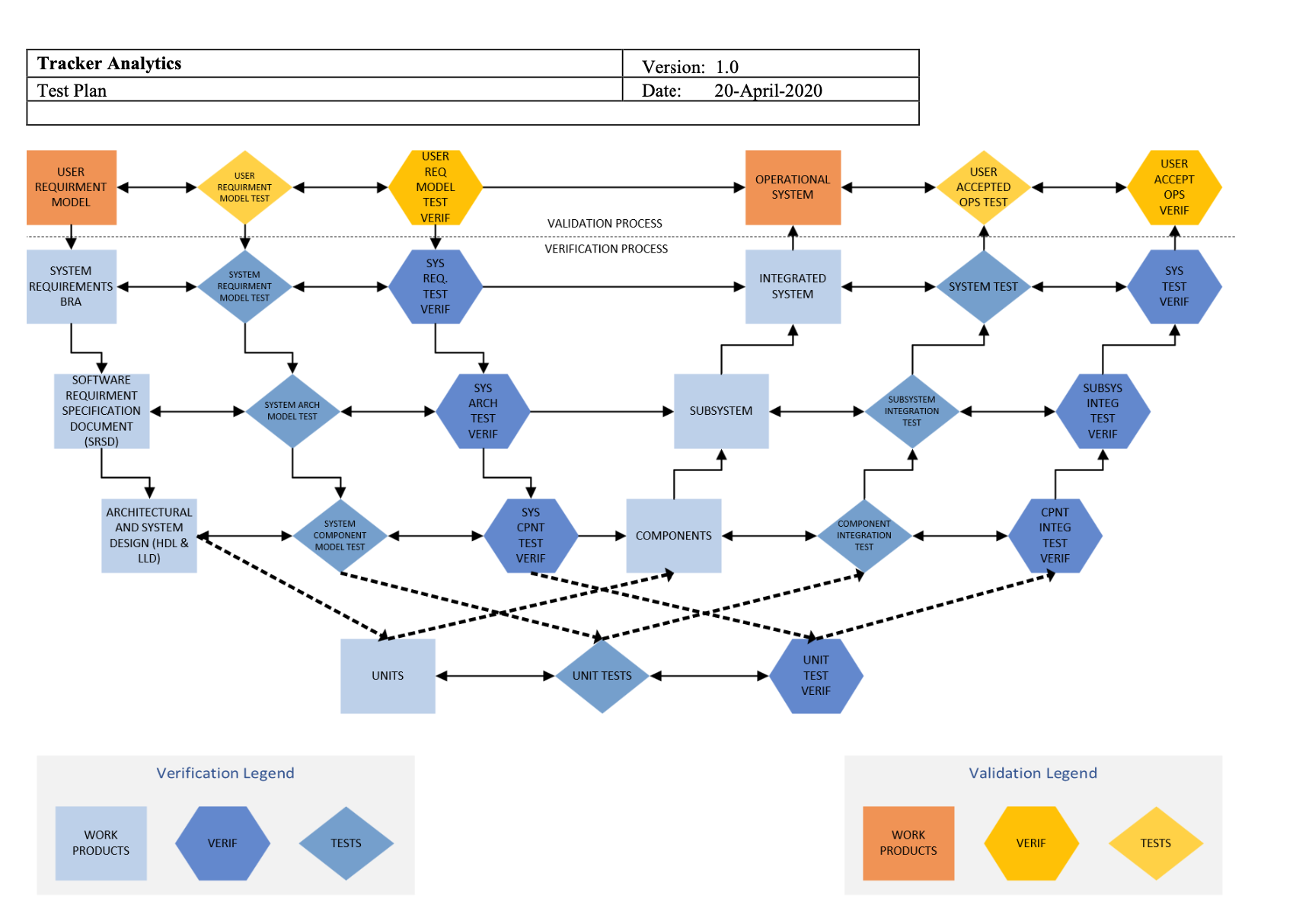
As part of the requirement engineering assignment, I worked with five other students in developing stakeholder’s interview questions, the vision document, and requirement artifacts. We discussed and researched on how to develop the materials. During our research in developing a Tracker Analytics product, we decided to use the Azure government cloud since it provides all the necessary standards that a government requires to deploy and use the software we developed. In our architecture, we incorporated microservices technology to allow for the application to scale up or down based on the demand and as well as utilizing the single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).

Software engineers are required to be honest and ethically responsible for upholding the law and follow a set of morally correct principles. below is the Software Engineering Code of Ethics and Professional Practice (Short Version).
The short version of the code summarizes aspirations at a high level of the abstraction; the clauses that are included in the full version give examples and details of how these aspirations change the way we act as software engineering professionals. Without the aspirations, the details can become legalistic and tedious; without the details, the aspirations can become high sounding but empty; together, the aspirations and the details form a cohesive code. Software engineers shall commit themselves to making the analysis, specification, design, development, testing and maintenance of software a beneficial and respected profession. In accordance with their commitment to the health, safety and welfare of the public, software engineers shall adhere to the following Eight Principles (ACM, n.d.):
-
PUBLIC
-
CLIENT AND EMPLOYER
-
PRODUCT
-
JUDGMENT
-
MANAGEMENT
-
PROFESSION
-
COLLEAGUES
-
SELF
Software engineers shall act consistently with the public interest.
Software engineers shall act in a manner that is in the best interests of their client and employer consistent with the public interest.
Software engineers shall ensure that their products and related modifications meet the highest professional standards possible.
Software engineers shall maintain integrity and independence in their professional judgment.
Software engineering managers and leaders shall subscribe to and promote an ethical approach to the management of - software development and maintenance.
Software engineers shall advance the integrity and reputation of the profession consistent with the public interest.
Software engineers shall be fair to and supportive of their colleagues.
Software engineers shall participate in lifelong learning regarding the practice of their profession and shall promote an ethical approach to the practice of the profession.
References
- ACM. (n.d.). The software engineering code of ethics and professional practice. Retrieved from https://ethics.acm.org/code-of-ethics/software-engineering-code/
- Microsoft. (n.d). What are the Mirosoft SDL practices? Retrieved from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/securityengineering/sdl/practices
- Mougoue, E. (2017, July 25). SSDLC 101: What is the secure software development life cycle? Retrieved from https://dzone.com/articles/ssdlc-101-what-is-the-secure-software-development
- The SAMM Project team. (2020, January 31). OWASP SAMM Version 2 – Public Release. Retreived from https://owaspsamm.org/blog/2020/01/31/samm2-release/
Risk Management Related Links
- Developing Cyber Resilient Systems: A Systems Security Engineering Approach – NIST SP 800-160 Rev 2
- OWASP SAMM Version 2 – Public Release
- SafeCode: Fundamental Practices for Secure Software Development
- System Security Engineering – NIST SP 800-160 Vol 1
- The Software Engineering Code of Ethics and Professional Practice – (ACM Ethics)
- What is the secure software development life cycle
- What are the Microsoft SDL practices
- Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations
- Volume II: Appendices to Guide for Mapping Types of Information and Information Systems to Security Categories